Abstract
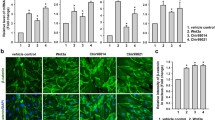
The problem of the currently used routine genotoxicity tests is relatively low predictivity of in vitro tests for in vivo genotoxicity and carcinogenicity. An important reason is considered to be inadequate expression of xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes in indicator cell lines. The aim of our study was to generate metabolically active differentiated hepatic progenies (hDHP) from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hASC) for genotoxicity testing. hDHP, generated using a three-step hepatic differentiation procedure, expressed hepatic properties such as glycogen storage and albumin secretion. The results of the comet assay demonstrated comparable sensitivity of hASC and hDHP to detect DNA damage induced by a direct acting genotoxic agent tert-butylhydroperoxide. Exposure to model indirect acting genotoxins benzo(a)pyrene, aflatoxin B1, and 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine did not induce DNA damage in hASC, while hDHP cells detected DNA damage induced by benzo(a)pyrene and aflatoxin B1, indicating their metabolic activity. The gene and protein expression analysis confirmed the presence of key enzymes involved in metabolism of the three genotoxins in hDHP cells. Moreover, the exposure of hDHP to the model pro-carcinogens altered the expression of selected metabolic genes. hDHP were further immortalized with hTERT transfection, resulting in a stable cell line that can be matured to metabolically active hDHP ready for genotoxicity testing in only 2 weeks. The advantage of these immortalized cells is their prolonged replicative life span and consequently limitless supply of hDHP cells. We conclude that hDHP cells have a great potential for the application in the routine genotoxicity testing and are therefore worth further investigations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson TB, Ingelman-Sundberg M (2008) Livers cells derived from human embryonic stem cells—progress and potential use in ADMET applications. Drug Discov Today Technol 5:e143–e147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddtec.2008.09.001
Arlt VM, Stiborová M, Henderson CJ et al (2008) Metabolic activation of benzo[a]pyrene in vitro by hepatic cytochrome P450 contrasts with detoxification in vivo: experiments with hepatic cytochrome P450 reductase null mice. Carcinogenesis 29:656–665. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgn002
Banas A, Teratani T, Yamamoto Y et al (2007) Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells as a source of human hepatocytes. Hepatology 46:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21704
Counter CM, Hahn WC, Wei W et al (1998) Dissociation among in vitro telomerase activity, telomere maintenance, and cellular immortalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14723–14728. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.25.14723
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I et al (2006) Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8:315–317. https://doi.org/10.1080/14653240600855905
George S, Heng BC, Vinoth KJ et al (2009) Comparison of the response of human embryonic stem cells and their differentiated progenies to oxidative stress. Photomed Laser Surg 27:669–674. https://doi.org/10.1089/pho.2008.2354
Ghaderi M, Allameh A, Soleimani M et al (2011) A comparison of DNA damage induced by aflatoxin B1 in hepatocyte-like cells, their progenitor mesenchymal stem cells and CD34(+) cells isolated from umbilical cord blood. Mutat Res 719:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2010.09.005
Guengerich FP, Johnson WW, Shimada T et al (1998) Activation and detoxication of aflatoxin B 1. Mutat Res 402:121–128
Hewitt NJ, Lechón MJG, Houston JB et al (2007) Primary hepatocytes: current understanding of the regulation of metabolic enzymes and transporter proteins, and pharmaceutical practice for the use of hepatocytes in metabolism, enzyme induction, transporter, clearance, and hepatotoxicity studies. Drug Metab Rev 39:159–234. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602530601093489
Kamdem LK, Meineke I, Gödtel-Armbrust U et al (2006) Dominant contribution of P450 3A4 to the hepatic carcinogenic activation of aflatoxin B1. Chem Res Toxicol 19:577–586. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx050358e
Khoury L, Zalko D, Audebert M (2016) Evaluation of four human cell lines with distinct biotransformation properties for genotoxic screening. Mutagenesis 31:83–96. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/gev058
Kim J, Kang JW, Park JH et al (2009) Biological characterization of long-term cultured human mesenchymal stem cells. Arch Pharm Res 32:117–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1125-1
Kirkland D, Pfuhler S, Tweats D et al (2007) How to reduce false positive results when undertaking in vitro genotoxicity testing and thus avoid unnecessary follow-up animal tests: report of an ECVAM Workshop. Mut Res 628:31–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2006.11.008
Kirkland D, Kasper P, Martus HJ, Muller L, van Benthem J, Madia F, Corvi R (2016) Updated recommended lists of genotoxic and non-genotoxic chemicals for assessment of the performance of new or improved genotoxicity tests. Mut Res 795:7–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2015.10.006
Knasmüller S, Parzefall W, Sanyal R et al (1998) Use of metabolically competent human hepatoma cells for the detection of mutagens and antimutagens. Mutat Res 402:185–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0027-5107(97)00297-2
Knasmüller S, Schwab CE, Land SJ et al (1999) Genotoxic effects of heterocyclic aromatic amines in human derived hepatoma (HepG2) cells. Mutagenesis 14:533–540
Kološa K (2016) Optimization of human mesenchymal stem cells production and their mutual interactions with tumour cells. Dissertation, University of Ljubljana
Kološa K, Motaln H, Herold-mende C et al (2015) Paracrine effects of mesenchymal stem cells induce senescence and differentiation of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Cell Transplant 24:631–644
Le Hegarat L, Dumont J, Josse R et al (2010) Assessment of the genotoxic potential of indirect chemical mutagens in HepaRG cells by the comet and the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assays. Mutagenesis 25:555–560. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/geq039
Lee SW, Min SO, Bak SY et al (2015) Efficient endodermal induction of human adipose stem cells using various concentrations of Activin A for hepatic differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 464:1178–1184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.07.100
Liang X, Chen X, Yang D et al (2012) Differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells by hTERT gene transfection in vitro. Cell Biol Int 36:215–221. https://doi.org/10.1042/CBI20110350
Mahmoudifar N, Doran PM (2010) Chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells in polyglycolic acid mesh scaffolds under dynamic culture conditions. Biomaterials 31:3858–3867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.090
Majer BJ, Mersch-Sundermann V, Darroudi F et al (2004) Genotoxic effects of dietary and lifestyle related carcinogens in human derived hepatoma (HepG2, Hep3B) cells. Mutat Res 551:153–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.02.022
Mihara K, Imai C, Coustan-Smith E et al (2003) Development and functional characterization of human bone marrow mesenchymal cells immortalized by enforced expression of telomerase. Br J Haematol 120:846–849
Natarajan AT, Durroudi F (1991) Use of human hepatoma cells for in vitro metabolic activation of chemical mutagen/carcinogens. Mutagenesis 6:399–403. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/6.5.399
Pelkonen O, Turpeinen M, Hakkola J et al (2008) Inhibition and induction of human cytochrome P450 enzymes: current status. Arch Toxicol 82:667–715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0332-8
Pezdirc M, Bojana Ž, Filipič M (2013) Genotoxicity and induction of DNA damage responsive genes by food-borne heterocyclic aromatic amines in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Food Chem Toxicol 59:386–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.06.030
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck S et al (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284:143–147. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5411.143
Richert L, Liguori MJ, Abadie C et al (2006) Gene expression in human hepatocytes in suspension after isolation is similar to the liver of origin, is not affected by hepatocyte cold storage and cryopreservation, but is strongly changed after hepatocyte plating. Drug Metab Dispos 34:870–879. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.105.007708
Seo MJ, Suh SY, Bae YC, Jung JS (2005) Differentiation of human adipose stromal cells into hepatic lineage in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 328:258–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.12.158
Shimada T (2006) Xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes involved in activation and detoxification of carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 21:257–276
Snykers S, De Kock J, Rogiers V, Vanhaecke T (2009) In vitro differentiation of embryonic and adult stem cells into hepatocytes: state of the art. Stem Cells 27:577–605. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2008-0963
Stiborová M, Moserová M, Černá V et al (2014) Cytochrome b5 and epoxide hydrolase contribute to benzo[a]pyrene-DNA adduct formation catalyzed by cytochrome P450 1A1 under low NADPH:P450 oxidoreductase conditions. Toxicology 318:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2014.02.002
Taléns-Visconti R, Bonora A, Jover R et al (2006) Hepatogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue in comparison with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. World J Gastroenterol 12:5834–5845
Turesky RJ (2010) Heterocyclic aromatic amines: potential human carcinogens. In: Fishbein JC (ed) Advances in molecular toxicology. Elesvier BV, Amsterdam, pp 37–83
Ulvestad M, Nordell P, Asplund A et al (2013) Drug metabolizing enzyme and transporter protein profiles of hepatocytes derived from human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells. Biochem Pharmacol 86:691–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.06.029
Viegas O, Žegura B, Pezdric M et al (2012) Protective effects of xanthohumol against the genotoxicity of heterocyclic aromatic amines MeIQx and PhIP in bacteria and in human hepatoma (HepG2) cells. Food Chem Toxicol 50:949–955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2011.11.031
Vinoth KJ, Manikandan J, Sethu S et al (2014) Evaluation of human embryonic stem cells and their differentiated fibroblastic progenies as cellular models for in vitro genotoxicity screening. J Biotechnol 184:154–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.05.009
Waldherr M, Mišík M, Ferk F, Tomc J, Žegura B, Filipič M, Mikulits W, Mai S, Haas O, Huber JW, Haslinger E, Knasmüller S (2018) Use of HuH6 and other human derived hepatoma lines for the detection of genotoxins—new hope for laboratory animals? Arch Toxicol 92:921–934. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-017-2109-4
Wilkening S, Stahl F, Bader A (2003) Comparison of primary human hepatocytes and hepatoma cell line HepG2 with regard to their biotransformation properties. Drug Metab Dispos 31:1035–1042
Winter HK, Ehrlich VA, Grusch M et al (2008) Use of four new human-derived liver-cell lines for the detection of genotoxic compounds in the single-cell gel electrophoresis (SCGE) assay. Mutat Res 657:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2008.08.012
Yildirimman R, Brolén G, Vilardell M et al (2011) Human embryonic stem cell derived hepatocyte-like cells as a tool for In Vitro hazard assessment of chemical carcinogenicity. Toxicol Sci 124:278–290. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfr225
Yin L, Zhu Y, Yang J et al (2014) Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiated into hepatocyte-like cells in vivo and in vitro. Mol Med Rep 11:1722–1732. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.2935
Žegura B, Filipič M (2004) Application of in vitro comet assay for genotoxicity testing. In: Yan Z, Caldwell GW (eds) Optimization in drug discovery. Methods in pharmacology and toxicology. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 301–313
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Slovenian Research Agency: the research core funding P1-0254, the project J6730, and MR-JTomc. It was also supported by the hCOMET COST Action (CA15132).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomc, J., Kološa, K., Žegura, B. et al. Adipose tissue stem cell-derived hepatic progenies as an in vitro model for genotoxicity testing. Arch Toxicol 92, 1893–1903 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2190-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2190-3